In the process of financial and economic activities, the enterprise has a need to settle accounts with its counterparties. When shipping products, performing work, or providing services, an enterprise, as a rule, does not receive money in payment immediately (sale on credit). Therefore, during the period from the moment of shipment of products or provision of service to the moment of receipt of payment, the company’s funds are recorded in the form of accounts receivable.
The level of accounts receivable is determined by many factors: the type of product, market capacity, the degree of market saturation with this product, the terms of the contract, the settlement system adopted at the enterprise, etc. Accounts receivable management involves its accounting, analysis, and control, as well as the determination of methods for accelerating the collection of debts and their reduction. Today, we will review the aging of accounts receivable.
Definition
The allowance method can be used to estimate the amount of bad debt expense to be recorded in the accounting books. According to this method, the amount of the reserve for doubtful debts is calculated by multiplying the balance of the debt at the beginning of the period by the coefficient of doubtfulness (probability of not collecting the debt).
This is a statistical method. When using it, it is not necessary to analyze the data of each specific debtor – it is enough to have statistics for the business as a whole for several periods, on the basis of which the probability of not being able to collect the money is calculated by the company for several consecutive periods. Therefore, this method cannot be applied to newly created businesses.
Under this method, there are three ways to do this estimation:
- Percent of sales method
- Percent of receivables method
- Aging of receivables method.
The aging of accounts receivable method calculates the adjusted balance of the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts. Since it focuses on the Balance sheet account Allowance for Doubtful Accounts, you might also see it referred to as the balance sheet approach. This method calculates what the adjusted balance in this account should be. A Bad Debt Expense is then recorded to make that balance correct.
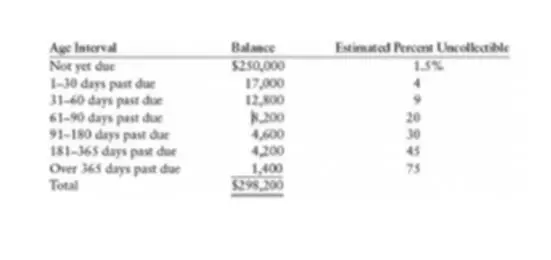
Usually, this method starts with a table. The receivables aging report does not have a specific format one has to follow. However, it is usually a table in which the receivables are categorized according to their payment terms. For example, the condition of a sale on credit “net 30” means that the debtor is granted a grace period of 30 days. If the invoice is not paid during this period, then after its expiration, it will be considered overdue. Typically, overdue receivables are classified into the following periods: 1-30 days, 31-60 days, 61-90 days, and over 90 days.
Example
In this example, we can see a company’s report on the debts of its clients and when they are due. Note that it chose to extend the overdue receivables time up to 120+ days. For convenience, the invoice number and the total amount due by each customer (Amount Receivable) are also included in the table. Now, the business management can see what their situation is looking like with each customer at a glance and calculate bad debt allowance based on this information.
To prepare such a table, you would need to go over your business bookkeeping records and write down all the customers who owe you. Along the way, you would be writing down the amount owed in the column corresponding to the time the clients have left to pay the debt. Finally, just total all the numbers for each client. Alternatively, you can just prepare a report that looks like the table below, compiling all your customers into one group and categorizing their debts by the time the debts are overdue.