For any commercial organization, the main goal is to maximize profit from their activities. For this reason, owners are always interested in the value of the retained earnings. Retained earnings are an inevitable part of every business. These are the means that the company can distribute between the founders or save on the accounts of the company for its subsequent development.
This remaining profit is essential for any company, therefore, in this article we will discuss how it is reflected in the balance sheet and what are the nuances associated with it, including its normal balance and what makes retained earnings go up and down.
After all, company managers should be aware of what is included in retained earnings and how they are recorded, although this is more likely to be related to the work of an accountant. But it is this line in the balance sheet that has a significant influence on the development of the company, helps it to move forward. Retained earnings are an ideal long-term source of business financing.
The normal balance of retained earnings
The normal balance in the retained earnings account is a credit. This balance signifies that a business has generated an aggregate profit over its life. However, the amount of the retained earnings balance could be relatively low even for a financially healthy company, since dividends are paid out from this account. Consequently, the amount of the credit balance does not necessarily indicate the relative success of a business.
When the balance in the retained earnings account is negative, this indicates that a business has generated an aggregate loss over its life. This is especially common during the startup years of a business, when it may incur sustained losses before the entity has accumulated enough customers and released enough products to ensure itself of a reasonable profit.
What are Retained Earnings?
Retained means to keep and earnings mean income, thus retained earnings is the percentage or amount of net income that was not paid in the form of dividends but was left in the company to reinvest in operating activities or pay debt obligations. These reserves earnings are a very flexible internal source of business financing because stockholders are in complete control.
Retained earnings are part of the stockholder’s equity on the balance sheet. It is a financing activity, and it is earned the capital portion of the stockholder’s equity. They’re also one of the items that connect the balance sheet and the income statement. This account is affected by net income, which involves all the activities that encompass investing business and liabilities that are part of the financing activity, and dividends paid.
But what are retained earnings in numerical terms? The retained earnings are calculated by adding retained earnings of a past period to the net income of the current period (or deducting in case of losses), as well as subtracting the dividends paid. As you can see, this is a cumulative amount – it accumulates since the company starts to the current date. It should be noted that this amount can be calculated after all of a company’s obligations have been met and paid, including the dividends it has declared for this period/year. So, how to prepare retained earnings statement use this a simple formula.
Retained earnings formula:
+ Beginning retained earnings (taken from previous retained earnings statement or balance sheet)
+ Net income during the period (taken from the net income statement for the current period)
– Dividends paid (based on what’s declared)
= Ending retained earnings
In most cases, companies maintain a surplus of income to invest in those investment opportunities where the company can generate growth, for example, investments such as the purchase of new equipment or the cost of research and development of existing products can have a significant effect on the growth of the company. The amount of retained earnings is adjusted every time an adjustment is made to income or expenses.
What is the opposite for retained earnings? The answer would be empty pockets because they can also be harmful. This may be because the loss ratio of the current financial year is higher than the retained earnings of previous years. Ongoing losses erode any historical positive retained earnings balance. In such cases, the indicator of retained earnings is usually called deficit and has a debit balance. In instances where a company has a debit balance that exceeds the amount of contributed capital instead of a normal balance, which is credit, it faces a risk of bankruptcy.
Retained earnings formula:
+ Beginning retained earnings (taken from previous retained earnings statement or balance sheet)
+ Net income during the period (taken from the net income statement for the current period)
– Dividends paid (based on what’s declared)
= Ending retained earnings
In most cases, companies maintain a surplus of income to invest in those investment opportunities where the company can generate growth, for example, investments such as the purchase of new equipment or the cost of research and development of existing products can have a significant effect on the growth of the company. The amount of retained earnings is adjusted every time an adjustment is made to income or expenses.
What is the opposite for retained earnings? The answer would be empty pockets because they can also be harmful. This may be because the loss ratio of the current financial year is higher than the retained earnings of previous years. Ongoing losses erode any historical positive retained earnings balance. In such cases, the indicator of retained earnings is usually called deficit and has a debit balance. In instances where a company has a debit balance that exceeds the amount of contributed capital instead of a normal balance, which is credit, it faces a risk of bankruptcy.
Net Income vs. Retained Earnings
Net income- part of the balance sheet profit of the enterprise remaining at its disposal after payment of taxes, fees, deductions, and other obligatory payments. Net income is used to increase the working capital of the enterprise, the formation of funds and reserves, and reinvestment in production. The volume of net income depends on the size of gross profit and the amount of taxes; based on the quantity of net income, dividends to shareholders of the enterprise are calculated.
Retained earnings can be invested in fixed assets, can also be stored in the form of cash balances or suitable for circulation on the securities market, used to finance the absorption of other companies, to extend loans to customers, to repay loans or to increase liquid assets. Retained earnings of the reporting year are part of the net profit that was not distributed by the organization in the reporting year. This indicator reflects the final financial result of the organization in the reporting year. The benefits and drawbacks of reserved income are as follows:
Benefits:
- Flexibility
- Business owners in control
- Low cost
- Can be substantial
Drawbacks:
- A drain on finance is loss-making
- The danger of hoarding profits
- The opportunity cost for shareholders
Retained Earnings on Balance Sheet
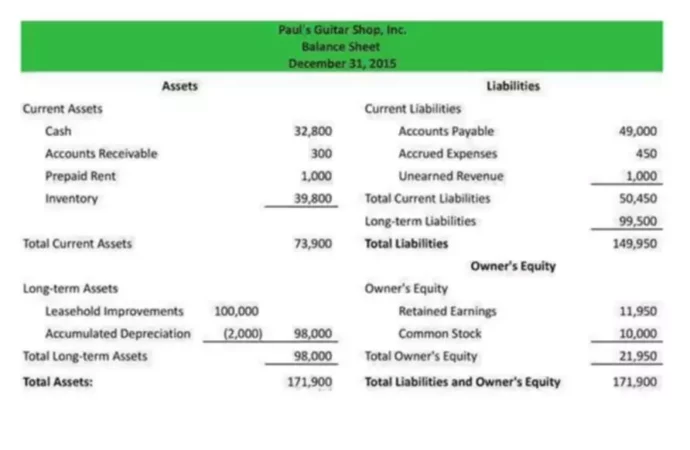
A balance sheet is an essential component of the organization’s annual reporting. The balance sheet is one of the five components of the annual accounting statements. The balance sheet contains data on the assets, liabilities, and equity of the organization. At its core, it is a document that reflects the property and financial condition in a certain period.
The balance consists of two parts – asset and liability. The asset reflects all the property that belongs to the organization and the debts of the counterparties (fixed assets, intangible assets, inventories, receivables, cash, etc.). In the liabilities, a section is the sources from which assets appeared (equity, borrowed funds, and external liabilities).
Retained earnings in the balance sheet are a liability because the value of this indicator shows the direct debit of the organization to its founders. Ideally, this amount is distributed among the shareholders and invested in the further development of the business. The company does not have the right to dispose of its retained earnings until the owners of the organization make an appropriate decision.
On the balance sheet, this account falls under Stockholder’s Equity. Stockholder’s equity is the aggregate of all the assets of the company that is in its ownership. It is the amount of authorized, reserve and additional capital, as well as retained earnings.
Typically, retained earnings balance increases as net income that is left after paying dividends are being added. However, this is not always the case. It is worth noting that the net loss should also be located in the liabilities side of the balance sheet, but in this case, we are talking about a negative value, and therefore the number will need to be taken in parentheses. But what is retained earnings normal balance?
How Is Retained Earnings Account Decreased and Increased?

So, what increases and decreases an account? It depends on the account. Some accounts increase with debits, while other accounts increase with credits. An example of statements that increase with assets includes assets, expenses, and withdrawals. Other reports, on the other hand, increase with loans, and this would consist of revenue accounts, liability accounts, and capital accounts.
When an account increases with a credit, we can say that its normal balance is credit. The normal balance in the retained earnings account is a credit. This means that if you want to increase the retained earnings account, you will make a credit journal entry. A debit journal entry will decrease this account. What are possible transactions that can affect retained earnings account?
Debit (decreases):
- Net loss
- Cash or scrip dividends
- Prior period adjustments (error corrections, etc. correct overstated income)
- Specific changes in accounting principle that results in previous years income overstatement
- Stock and Property dividends
- Extraordinary losses
- Treasury Stock and Stock retirement transactions
Credit (increases):
- Net Gain
- Prior period adjustments (error corrections, etc. correct understated income)
- Specific changes in accounting principle that understates previous years income
- Adjustments due to quasi-reorganization
- Extraordinary gains
- Appropriated retained earnings
- Differences from cost method to equity method to account for investments
In summary, the two main activities that affect retained earnings are net income for the year or period and any dividends paid. Let’s look at how net income affects retained earnings. Net income consists of revenues, expenses, and cost of goods sold. For example, if a company had revenues of $1,000, $100 in payments and the cost of goods sold equals to $200, then net income will equal to 1,000 – 100 – 200 = $700.
The $700 gain will increase the retained earnings by crediting the account. If the net income were a loss, the retained earnings account would be debited to decrease it. Now, let’s look at the other factor – dividends paid. As you are already aware, dividends payout reduces the retained earnings account. Thus, if a company declares dividends, say $300, then this amount will be debited to the retained earnings account, decreasing it.
What do we have as a result? Let’s say the company had $200 retained earnings from the previous period, then we credited $700 of net income and debited $300 of dividends paid. Thus, we get a net amount of $600 – a credit balance, which is a normal balance for this account. If the company had a net loss higher than $200, the result would be negative retained earnings, accumulated deficit, that appear as a debit balance in the retained earnings account, rather than the credit balance that appears typically for a profitable company.

















