Definition
One of the main distinguishing features of management accounting is its focus on the current and future activities of the enterprise. For financial management accounting, financial planning, which is also traditionally called budgeting, is responsible for the present and the future.
A budget report is an annual financial plan of an organization, which is a formalized statement of the intentions of management in relation to sales, expenses, and other financial actions for the coming year. The budget report is both a planning tool and a control tool: at the very beginning of the period, the budget is a plan or standard; at the end of the period, it serves as a control data that management can use to determine the effectiveness of actions and plan actions to improve the organization’s performance in the future.
From a financial point of view, budgeting is nothing more than the preparation of a budget report for future reporting periods as well as a constant process of clarifying these plans, comparing planned data with actual data, and analyzing the reasons for discrepancies. In the process of budgeting, not only the financial department and top management get involved, but also all divisions and structural units of the enterprise.
The advantages of budgeting are presented in short-term and long-term planning of the organization’s resources, the behavior of competitors, and especially the current and projected market demand for products. For these strategic aspects, plans are developed and budgets are formed at all levels and at different intervals.
Computer-aided budgeting can be helpful in evaluating different “what-if” options. This analysis makes it easier for management to find the best course of action among the possible alternatives. If the management does not like something in the future financial statements, then it can change the planned proposed actions and decisions.
The budget can be drawn up both in value (dollar amounts) and quantity (units produced). It is advisable that the forms of budgets and accounting reports coincide, as this increases the efficiency of control over their execution. More precisely, the same items and other analytics should be used for management financial reporting and budgeting.
Purpose
The main goal of budget reports is to improve the efficiency of the enterprise. Efficiency is enhanced by the following:
- In a report, we bring together many financial items associated with the formation of income and costs. You will see a complete picture of how each dollar appears at the business and where it goes.
- Companies can prepare budgets for departments. Part of the responsibility is removed from the business owner and managers have the opportunity to manage the revenues and costs of their departments within the framework of the budget report of the company.
- The worker will have a roadmap laid out for them and goals to reach, which will motivate them to do their best.
- Budgeting will help you achieve all the functions of financial management – accounting, analysis, planning, organization, motivation, regulation.
- Work with finances is carried out in real-time! We take into account the plan for the production of products, schedules of repayment of accounts payable, staffing.
Types
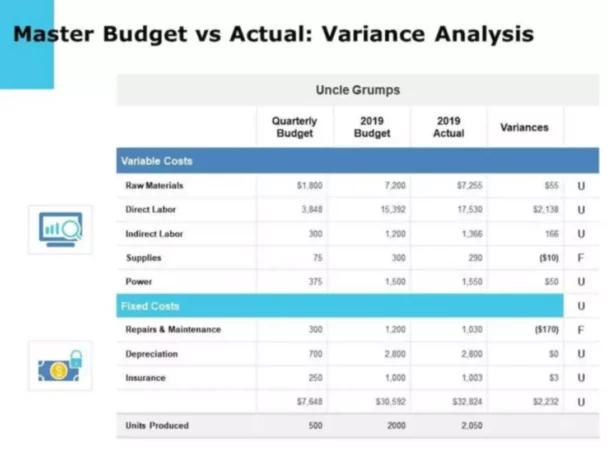
There are different types of budget reports, static and flexible being the most common ones. A static budget report is a solid plan in which income and expenses are planned based on a given sales volume only. The execution of this type of budget is controlled by actual indicators without adjustments.
A static budget makes it possible to assess only absolute indicators of budget execution. It reflects the fact of the result obtained. This type of budget is used in spheres where work does not depend on the volume of production or sales of products. A static budget is usually designed for a specific level of business activity in an organization. It cannot be used to control costs when the activity level changes. It is impossible to carry out a detailed analysis of the performance of an organization using a static budget. Therefore, in practice, a flexible budget is used more often.
The flexible budget provides for several alternative options for the volume of sales and all kinds of adjustments to costs and revenues depending on changes in volumes. If indicators are planned in a static budget, then in a flexible budget report one they are calculated. A flexible view of budgets provides more objective data for analyzing the implementation of planned targets. A flexible budget can be used both for planning and for analyzing and evaluating various business situations in the face of possible unforeseen circumstances. At the heart of building a flexible budget is the division of costs into fixed and variable costs.